At TheHealthBoard, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
How does the Spinal Cord Function?
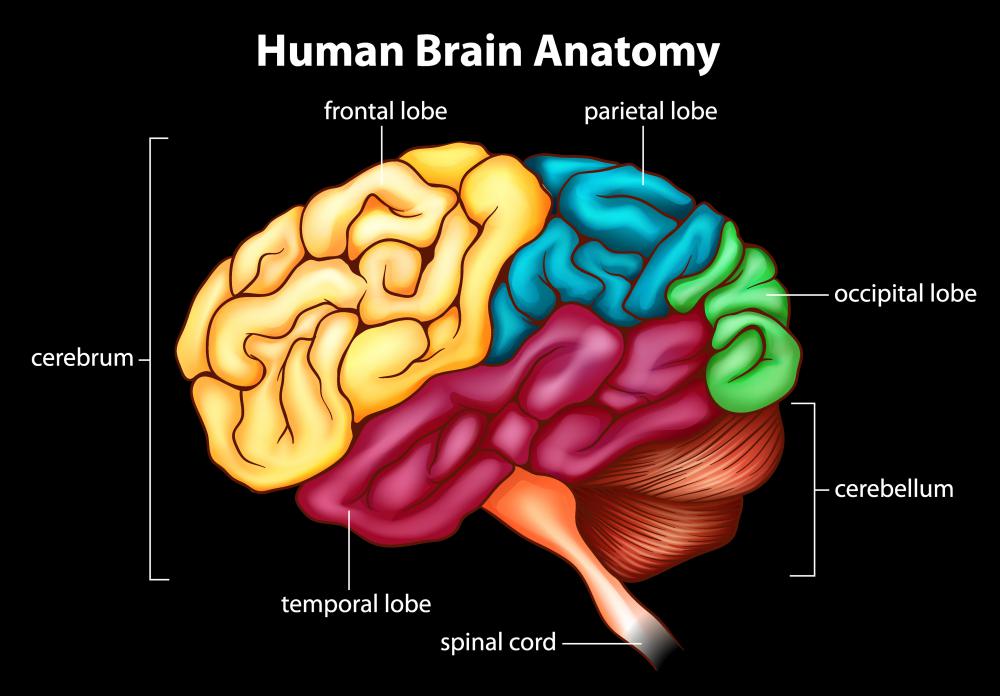
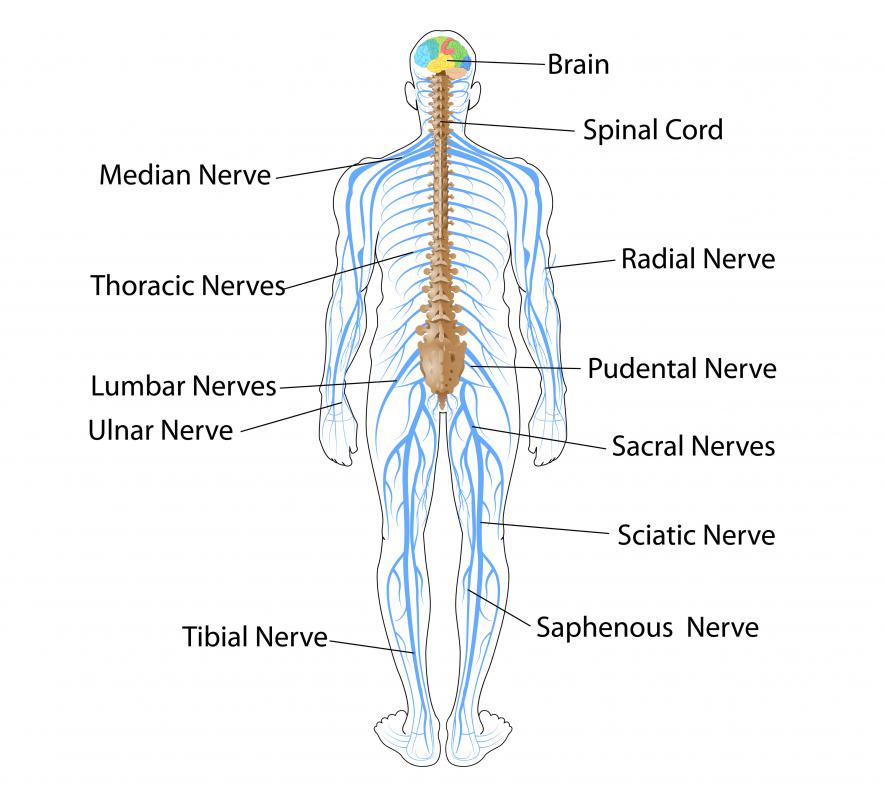
The spinal cord is a track of nerves in the back. This crucial member of the central nervous system utilizes nerve cells and nerve tracts to function in several important ways. Vital spinal cord functions include providing a brain-body connection, directing movement, and housing the body’s reflex system.
Several parts compose the spinal cord, and each plays a crucial role in spinal cord function. Nerve cells are contained in gray matter in the spinal cord, and this matter surrounds an inner canal filled with spinal fluid that provides the cord with density and a cushion. The tracts that lead to and from the brain reside within an outer layer of white matter. These tracts are made of sensory and motor neurons. Three layers of membrane tissue and protective vertebrae bones encase the delicate nerves vital to spinal cord function.

Segments of the spinal cord give rise to pairs of spinal nerves that branch from the cord. The roots of these nerves communicate with other cells within the central nervous system. They then help transfer this information to other nerves throughout the body. In turn, incoming information from the peripheral nervous system makes its way to the brain via these nerves. The most important spinal cord function is this gateway between the brain and the rest of the body.

Brain-and-body interaction means another vital spinal cord function is its ability to coordinate body movements. The sensory neurons found within the spinal cord respond to the body’s five senses and convert stimuli from the outside environment into electrical impulses. These impulses are then sent to the central nervous system for processing. In turn, motor neurons convert central nervous system information into electrical impulses that are directed to muscles and organs, thus controlling movement. If any section of the spinal cord is injured, body paralysis can result.

The spinal cord also contains the reflex arc. When receptor nerves in the skin are triggered by an extreme sensory stimulus such as intense heat or burning, the receptors send a warning impulse to the spinal cord. Further, motor or gland nerves that connect to the spinal cord unleash a reflex depending on the type of stimulus. Reflexes can either affect the skeletal system or the heart and other organs. Its role in these instinctual responses means the spinal cord is crucial in the nervous system’s fight-or-flight response pattern.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:













Discuss this Article
Post your comments