At TheHealthBoard, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What are Microvilli?
From the Greek for “tiny” and the Latin for “shaggy hair,” the term microvilli refers to microscopic protrusions on the surface of certain cells of the body. Some microvilli are specialized parts of sensory organs, such as, the ear, tongue, and nose. Others assist internal organs to function properly. These tiny structures can enlarge the surface of a cell 600 times its original size, increasing its ability to secrete or absorb.
In the inner ear, microvilli — called stereocilia — in the cochlea are instrumental in hearing. These miniscule filaments detect sound and transmit auditory information to the auditory nerve. As humans age, they typically experience hearing loss, often due to damage of these tiny hairs. Factors that might damage or destroy these essential cellular outpocketings in the auditory system include excessive noise such as heavy machinery, loud music, and jet engines. People who live and work in high decibel areas typically wear earplugs to protect the stereocilia.

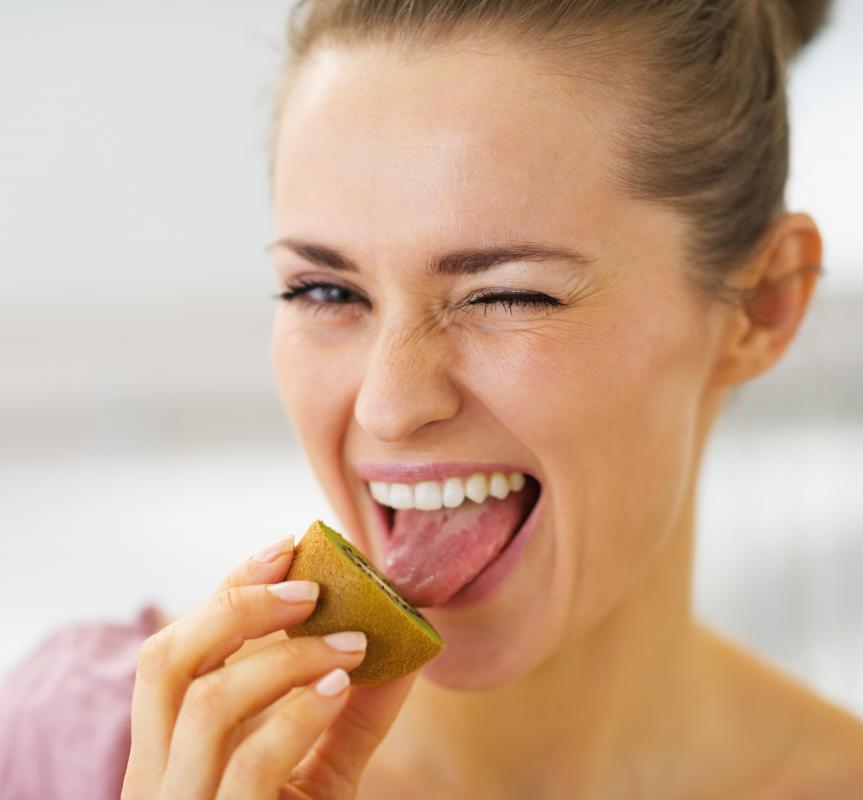
The top side of the human tongue also is covered with finger-like projections called papillae. These papillae contain the taste buds, which are made up of specialized microvilli. Each microvillus absorbs the taste — bitter, sweet, sour, and salty — and sends the information to the brain. The brain deciphers the message and determines whether to accept or reject the food or drink. Bitter foods, for example, can sometimes be dangerous to consume.

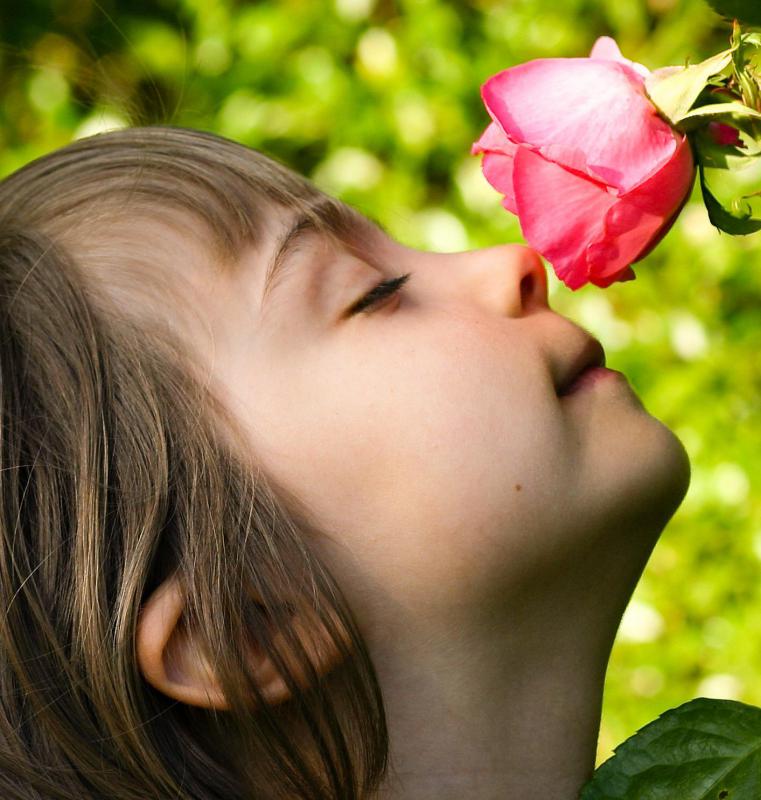
In the nose, olfactory receptor cells covered with microvilli absorb minute amounts of scent-laden moisture and transmit the information to the brain. As with hearing and taste, this sensory information is typically used by the brain to determine the safety of environmental stimuli. If food emits an unpleasant smell, for example, it might be unfit to consume. The detection of smoke might signal the danger of fire. On the other hand, microvilli may also assist in reproduction, as they might also detect the pheromones of a prospective mate.

Intestinal cellular protrusions also assist body systems to function properly. In the intestines, microvilli increase the surface area of digestive cells to help the intestines absorb every bit of nutrition gleaned from ingested food. They also increase the number and functionality of the enzymes that process carbohydrates. Microvilli appear in the proximal tubule of the kidney as a “brush border,” so-called because this close clustering of tiny outpocketings resemble the tip of a paintbrush under a light microscope. These nephritic microvilli act as mechanoreceptors, sending information to the brain about the kidneys.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:















Discussion Comments
Villi are folds in the small intestine while on a villis, there are lots of microvilli that increase the surface area. Therefore, it increases the efficiency of the absorption of nutrients -- by surface area.
@goldensky - I'm not an expert in the scientific field but if my memory serves me correctly the function of the microvilli is to maximize the organ for absorption such as the stomach or intestines.
The cilia are located in the respiratory system. Their function is mainly to move things along like pushing excess mucus up the trachea so you can cough it out.
That's the best way I can think of to explain it. I hope it helps.
Since both microvilli and cilia are both located in our digestive cells what makes them different from each other?
Post your comments