At TheHealthBoard, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What is External Resorption?
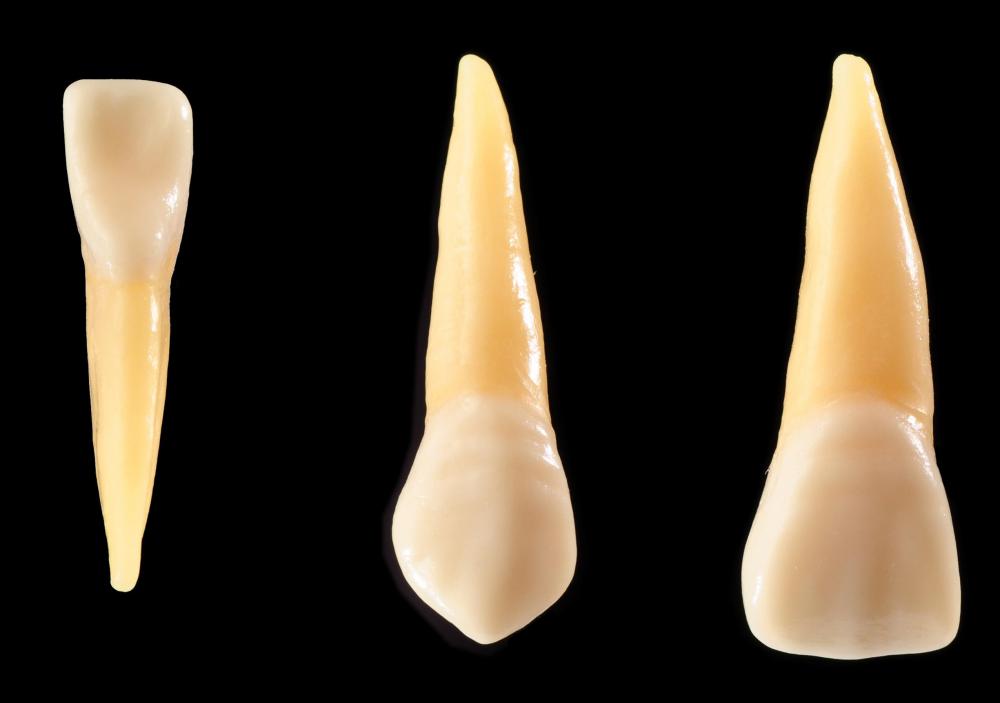
External resorption occurs when the surface of the root of a tooth becomes inflamed and the body attacks the root, causing it to be destroyed or dissolved. There are two types of resorption — internal and external. External resorption differs from internal, as the destruction of the tooth begins on the outside surface of the tooth, also known as the cementum, and then travels through the dental tissue to the root. This type of resorption is usually much more severe and almost always results in the tooth being extracted.
The cause of external resorption is sometimes unclear, but there are many situations that can cause a tooth's root to dissolve. Pressure from another tooth or orthodontic materials, for example, can cause trauma to the outside of the tooth, which is sometimes seen in children who have impacted wisdom teeth that are putting pressure on an emerging tooth. Bacteria resulting in infection or inflammation also can cause the body to attack and destroy the tooth. Additionally, trauma to the tooth caused by a violent hit can result in this condition — the body attempts to dissolve the broken parts of the tooth, which can end in the full resorption of the root.

Once the trauma has occurred to the tooth, osteoclasts, a type of cell that destroys bone tissue, attach to the surface of the root and begin to dissolve the outer layer of the tooth root. This process continues to the inner root of the tooth, destroying the blood vessels and nerve tissue, and causing the crown of the tooth to become loose and unstable. Tooth resorption occurs if the entire tooth, including the bone, ligament and crown, is affected.

Sometimes, the space left by the dissolved root tissue will be replaced by bone. The bone attaches to the tooth in a process called ankylosis. The bone will begin to turn the other surrounding dental tissue into bone as well, however, which can cause even more severe dental problems.
A tooth affected by external resorption almost always must be removed because the dissolving process can also spread to other surrounding teeth; a tooth with internal resorption may be saved through a root canal treatment, however. Once the tooth is removed, an implant will be put into place. A person with symptoms of external resorption should immediately contact a dentist for more information on external resorption and to determine a path of treatment.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:















Discussion Comments
My sorority sister got caught up in a bad relationship that ended with her taking a bat to the jaw. Her horrible boyfriend hit her on his way to baseball practice because he saw her talking to her male professor outside of the classroom.
Parts of the tooth became dislodged, and her body started dissolving them. She waited before going to a dentist out of shame for what she had allowed to happen to her. By the time she did go, the pain was so great that even an anesthetic could not deaden it. She had to have excruciating surgery.
Post your comments