At TheHealthBoard, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What Is Junctional Bradycardia?
Bradycardia is a condition where the heart beats slower than normal. A slow heart beat can actually be normal for some individuals such as athletes. For others, normal resting heart rate is 60 to 100 beats per minute. Bradycardia is a heart rate slower than 60 beats per minute. Those with the condition may experience symptoms such as dizziness, fatigue, shortness of breath and fainting.
In order to understand junctional bradycardia, it is helpful to first understand how the heart beats. Our heartbeat is caused by electrical impulses. The sinoatrial (SA) node is the heart's natural and primary pacemaker which sets a regular rate and rhythm by firing regularly. The atrioventricular (AV) node slows down the electrical signals before entering the ventricles. The electrical impulse reaches the muscular walls of the ventricles and causes them to contract. The heart beats and the cycle begins all over again.

A junctional rhythm occurs when the AV node is acting as the primary pacemaker of the heart. When the SA node fails to function, the AV node takes over resulting in several types of rhythm. Thus, when the AV node is functioning as the primary pacemaker of the heart and resulting in a resting heart rate of less than 60 beats per minute, this is called junctional bradycardia.

Just as with other forms of bradycardia, junctional bradycardia will cause symptoms like dizziness. The condition is diagnosed through an electrocardiography (ECG) which will present inverted P waves in the test results indicating a shift to the AV node.
Generally, treatment of bradycardia depends on the cause. For example, in cases where other medical problems or medications are resulting in bradycardia, treatment of other conditions or changing medication may be the required treatment.

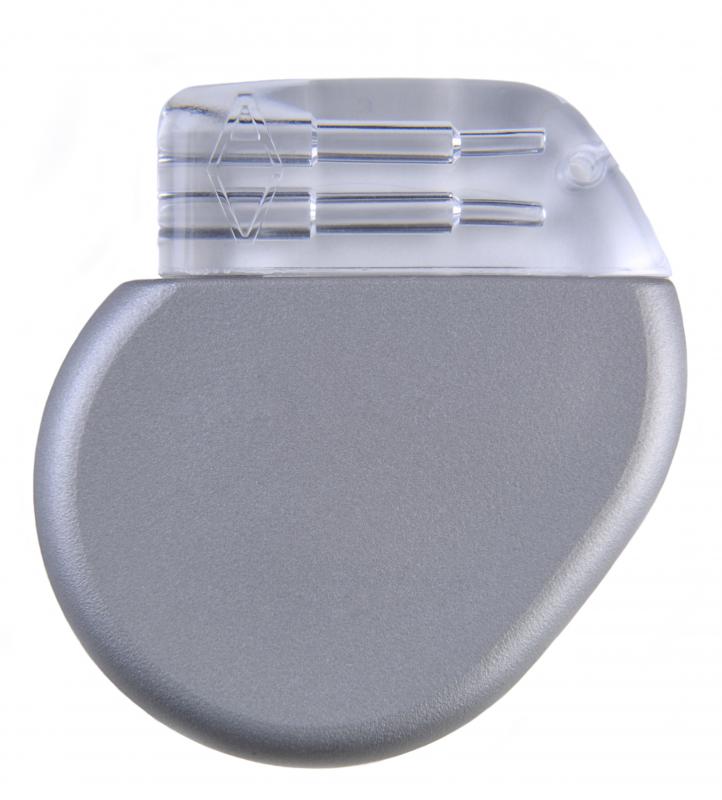
Since junctional bradycardia indicates damage to the electrical system of the heart, the preferred treatment may be a pacemaker. A pacemaker is a device that is planted under the skin and regularizes heart rate. Regular check-ups are required to make sure that the pacemaker is functioning correctly and those with the device must avoid strong electrical fields that may impact the impulses. Being told that a pacemaker is required may be alarming at first. But it's important to remember that there are many individuals with pacemakers and they continue to lead normal and healthy lives.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:












Discuss this Article
Post your comments