At TheHealthBoard, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What is Pulmonary Thrombosis?
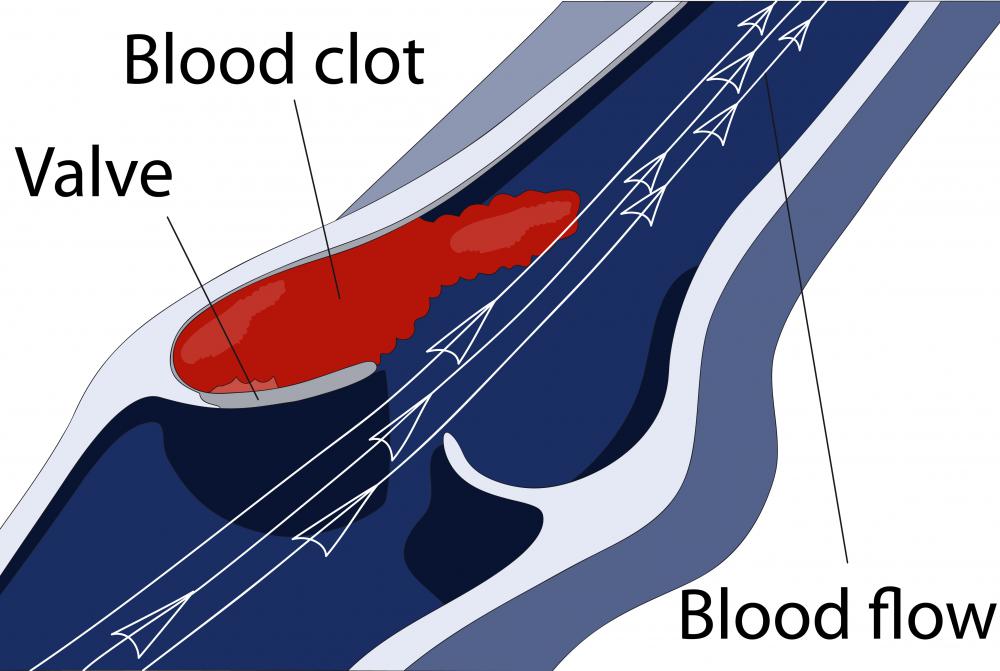
Pulmonary thrombosis is a blood clot that has formed in the body, often originally forming in one of the deep veins of the leg, and that has become lodged in one of the blood vessels of the lung. A diagnosis of pulmonary thrombosis is a potentially fatal emergency situation and requires prompt medical attention. Should the clot fully block a blood vessel and impede blood flow to the lung, that portion of lung can suffer a pulmonary infarct. The lung tissue will die because no oxygen-rich blood can reach the tissue.
A blot clot, called a thrombus, can form in one of the blood vessels or deep veins of the leg, arm or heart. Different types of thrombosis are named for their location in the body. Deep vein thrombosis is a blood clot in the deep veins of the leg, such as the femoral vein. Portal vein thrombosis affects the hepatic portal vein of the liver. With pulmonary thrombosis, the thrombus dislodges from somewhere within the circulatory system and travels through the vessels until it reaches the tiny capillaries or veins of the lungs.

Half of the patients who suffer pulmonary thrombosis exhibit no symptoms. The body might heal itself of the clot without the patient ever realizing his or her condition. A large clot or a clot blocking a critical blood vessel might cause severe symptoms of pulmonary thrombosis, such as shortness of breath, chest pain, heavy sweating, a lightheaded feeling or bloody sputum. Untreated pulmonary thrombosis can lead to permanent lung damage, low blood-oxygen levels or organ damage from a lack of oxygen. Symptoms are signs of a serious condition and call for immediate medical attention.

Treating pulmonary thrombosis depends on the condition's severity and cause, if known. In most non-emergency cases, physicians usually prescribe intravenous or oral anticoagulant drugs to thin the blood. Thrombolytics are prescribed to reduce the size of the clot. Critically ill patients are placed on oxygen and blood-thinning medication and might undergo a catheter procedure or major surgery to remove the clot.

Medical professionals are not completely sure what causes pulmonary thrombosis in some patients, but most professionals concur that reduced mobility and an inactive lifestyle contribute to the disease. Aging, extended immobility from injury or surgery, medical trauma or pregnancy can precipitate blood clots. Steps for preventing pulmonary thrombosis include treating patients with blood-thinning drugs before surgery, prescribing compression stockings after surgery and maintaining an active lifestyle.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:


















Discussion Comments
@burcinc-- Oh okay. So people with pulmonary thrombisis had an embolism at some point, because that blood clot had to reach the lung somehow.
My brother-in-law has a blood clot in his lung. It's not very bad right now and he's just being treated with anticoagulant medication. He keeps going in for check-ups though. He has been told to watch out for shortness of breath and chest pain. Hopefully, the blood clot will dissolve on its own.
Isn't pulmonary embolism also a blockage of a vein? What is the difference between pulmonary vein thrombosis and pulmonary vein embolism?
Post your comments