At TheHealthBoard, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What is Skeletal Muscle Contraction?
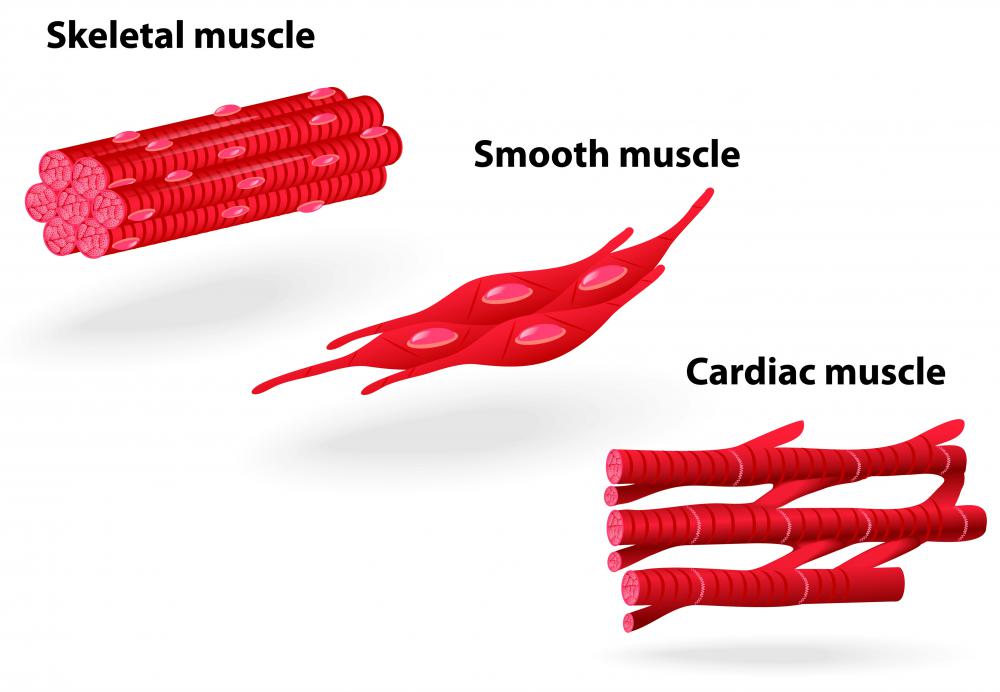
A skeletal muscle contraction is the mechanism by which muscles of the movable joints of the body produce movement at those joints. Skeletal muscle is differentiated from cardiac muscle, which pumps the heart, and smooth muscle, which is a component of several internal organs and produces movements like pushing food along the digestive tract, in that it connects at both of its ends to bone. As such, when it contracts — that is, when its fibers shorten and lengthen — it pulls on the two bones, causing motion at the joint it crosses. Skeletal muscle contraction, which involves a chemical reaction at the level of protein components contained within every muscle cell, is what makes movement of the skeleton possible.
There are a few different types of contractions that skeletal muscle can produce. A contraction in which the muscle fibers shorten, as seen when the rib cage is drawn closer to the pelvis during an abdominal crunch, is known as a concentric contraction. When the muscle fibers lengthen, as in the lowering phase of a crunch, an eccentric contraction is taking place. A skeletal muscle contraction involving both the concentric and eccentric phase of a movement is known as an isotonic contraction. An isometric contraction, on the other hand, is one in which the muscle does not change in length while contracting, as in holding a squat position without moving.

Skeletal muscle is made up of bundles of muscle fibers, which in turn are bundles of muscle cells. Muscle cells are long, narrow, and cylindrical in shape, and made up of units called sarcomeres that are responsible for skeletal muscle contraction. The model that explains what occurs in the sarcomere as a muscle contracts is known as sliding filament theory. It can be used to explain all types of muscle contraction, which differ only as a result of whether the force applied to the muscle is less than, greater than, or equal to the force produced by the muscle cells.

Within each sarcomere, a unit occurring in the hundreds of thousands in each muscle cell, are proteins organized into long filaments called actin and myosin. The actin proteins are passive, meaning that they form chains that receive the active myosin proteins. Arranged in alternating lines, the myosin slides back and forth past the actin, and in the process it emits calcium ions that cause each myosin protein to bind to a corresponding site on each actin protein.

During skeletal muscle contraction, the myosin filaments grab onto the actin and pull past it. This happens simultaneously in the cell’s many sarcomeres, which are arranged in bands. This “stroke,” as it is commonly known, causes a collective shortening of the muscle, which then returns to its resting length as the myosin releases itself from the actin.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:













Discuss this Article
Post your comments