At TheHealthBoard, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
What is the Relationship Between the Nucleus and Cytoplasm?
The nucleus and the cytoplasm are two very different parts of cells, but they also work together in a number of key ways, particularly where protein production and cell division are concerned. Nearly all cells, whether human, plant, or animal, have both of these elements. The nucleus is basically the “brain” of the cell, and is where all of the important data and cellular materials are housed. It looks sort of like the yolk in the center of an egg. The cytoplasm, by contrast, is more analogous to an egg white. It is the fluid that keeps the cell’s internal environment suspended, and the nucleus floats within it. Materials can and do pass from the cytoplasm into the nucleus and then from the nucleus back into the cytoplasm, but the process is highly regulated. Protein production is one of the most important things to require this sort of free passage, and is what allows cells to reproduce and grow. The contents of the nucleus don’t usually come into contact with the cytoplasm, but two scenarios — cell division and cell death — are exceptions.
Basics of Cell Organization

Cells are often more complex than their microscopic size might lead one to believe. The exact components vary between organisms, but certain elements, including the nucleus and cytoplasm, are more or less universal. A cell wall serves as the outer barrier, and holds the jelly-like fluid of the cytoplasm in place. The cytoplasm’s main job is to keep a temperatures and pressures constant, and to provide an easy way for different cell components to move around. The nucleus usually sits in the middle of the cytoplasm, and it, like the cell itself, is surrounded by a thick membrane wall inside of which sits all of the cell’s genetic material and essential proteins.
Understanding the Pieces Individually

The cytoplasm is crowded with fibers, tubules, passageways and compartments. It also contains fats, lipids, proteins and other useful molecules that the cell can use for doing whatever it is it is meant to be doing. Some cells are primarily involved in things like digestion, while others move particles and other cells from place to place; still more are members of the immune system and fight bacteria and other infections. These different tasks require different tools, and most of these are found floating in the cytoplasm.
Essentials of the Nucleus

The nucleus of the cell is usually a large, central organelle. It contains the chromosomes that hold the cell’s genes, or DNA. The nucleus is bound by a nuclear envelope, usually a double membrane, that separates it from the cytoplasm. It, too, is fluid filled, and has its own equivalent of the cytoplasm called the nucleoplasm.
The nuclear envelope is perforated with pores that allow molecules to enter and exit the nucleus. These pores are formed by a ring of proteins that hold the two membranes of the nuclear envelope together, and also regulate molecular traffic between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
Protein Production

The production of proteins, which control most of the cell's activities, is a two-step process that occurs in both the nucleus and the cytoplasm and is one of the most important ways in which these two cell components interact. DNA in the nucleus is read and coded into messenger RNA in a process called transcription. Messenger RNA, or mRNA, is a complex molecule that carries out the instructions of DNA. The mRNA leaves the nucleus and functions in the cytoplasm.
Once in the cytoplasm, mRNA goes through a process known as translation. Translation is the process of reading the mRNA and “translating” the information into amino acids. The amino acids are what ultimately make up proteins.
These proteins are essential to the nearly every cell’s function. Proteins provide cells structure, communication and transportation, and they form enzymes that are responsible for cell metabolism. In addition, they provide cell movement, play a role in recognition and protection, and bind cells to other cells. All of the activity that takes place in the cytoplasm is controlled by proteins that were coded by the nucleus. In this sense, the nucleus acts like the brain of the cell. Extending the analogy, the cytoplasm would represent the body that is controlled by the brain.
Nuclear Breakdown
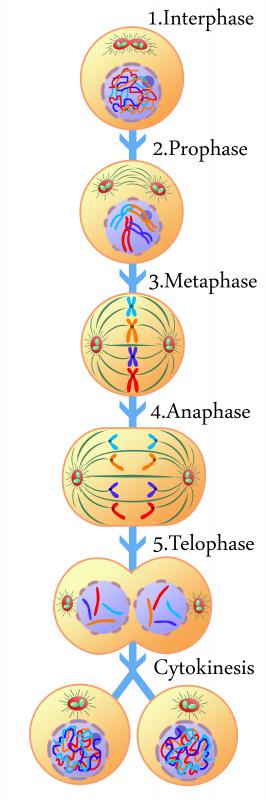
The nucleus and cytoplasm remain separate from each other the majority of the time. During cell division, known as mitosis, however, the nuclear envelope breaks down, and the genetic material spreads out into the cytoplasm. Cell division requires extra space to for the cell to duplicate and divide in two. A new nuclear envelope is formed in each new cell. Under usual circumstances, the only other time that the nucleus and cytoplasm come into direct contact with each other is during the death of the cell after the nuclear envelope disintegrates.
AS FEATURED ON:
AS FEATURED ON:













Discussion Comments
This is a very helpful and informational site. Thank you.
Post your comments